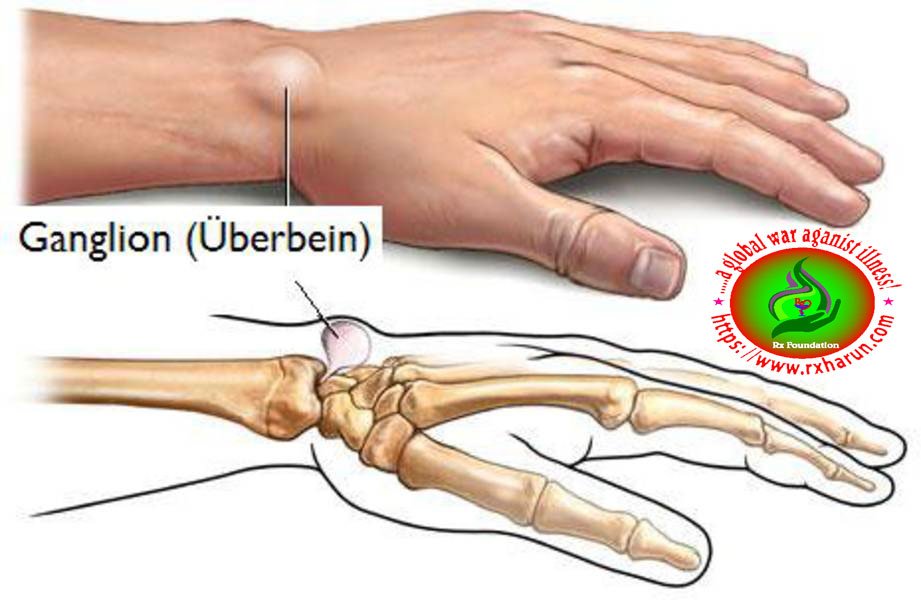
Wrist Ganglion is a fluid-filled or noncancerous lump associated with a joint or tendon sheath. They most often occur at the back of the wrist followed by the front of the wrist. Onset is often over months. Typically there are no further symptoms. Occasionally pain or numbness may occur. But some occur in the ankles or feet. When a ganglion cyst presses on a nerve it can be painful. And depending on its location, a ganglion cyst may restrict movement.
The ganglion cyst is the most common soft tissue swelling in hand and wrist. It occurs most commonly on the dorsal side of the wrist (70%), followed by volar side (20%) of wrist and tendon sheath of fingers. Most of the ganglion cysts are asymptomatic besides swelling. Most patients sought advice and treatment because of the cosmetic appearance or they were concerned that their ganglion was a malignant growth [1]. Treatment options include reassurance, nonsurgical means like aspiration with or without steroid injections or hyaluronidase and surgical excision. We review the treatment outcome of ganglion in the literature and compare their recurrence and complication rates.
Other Names of Wrist Ganglion
- Bible Bump (Ganglion Cyst)
- Bible Cyst (Ganglion Cyst)
- Gideon’s Disease
Types of Wrist Ganglion
Nishikawa et al developed a new arthroscopic classification of ganglia, which indicates how much dorsal capsule require resection. They were classified into three types:
- • Type 1 ganglia and their stalks were visible;
- • Type2a ganglia or their stalks ballooned into the wrist joint with external compression;
- • Type 2b ganglia or their stalks could not be identified in the wrist joint, even with external compression.19
Epidemiology of Wrist Ganglion
Incidence
- it is the most common hand mass (60-70%)
Location
- dorsal carpal (70%)
- originate from SL articulation
- volar carpal (20%)
- originate from radiocarpal or STT joint
- volar retinacular (10%)
- originate from herniated tendon sheath fluid
- dorsal DIP joint (mucous cyst, associated with Heberden’s nodes)
Causes of Wrist Ganglion
No one knows exactly what causes a ganglion cyst to develop. It grows out of a joint or the lining of a tendon, looking like a tiny water balloon on a stalk, and seems to occur when the tissue that surrounds a joint or a tendon bulges out of place. Inside the cyst is a thick lubricating fluid similar to that found in joints or around tendons.
Causes that may increase your risk of ganglion cysts include
- Your sex and age – Ganglion cysts can develop in anyone, but they most commonly occur in women between the ages of 20 and 40.
- Osteoarthritis – People who have wear-and-tear arthritis in the finger joints closest to their fingernails are at higher risk of developing ganglion cysts near those joints.
- Joint or tendon injury – Joints or tendons that have been injured in the past are more likely to develop ganglion cysts.
- Overuse – People who use certain joints vigorously are more likely to develop ganglion cysts. Female gymnasts, for instance, are particularly prone.
- Trauma – They may result from a single incident or from repeated small injuries.
- Joint stress – might lead to a split in the joint capsule that surrounds the joint. As a result, synovial fluid leaks into the tissue around the joint. Reactions between the fluid and tissue then create the thick cystic fluid and the cyst wall.
- Joint stress – may cause connective tissue to break down in the area. If fluid then accumulates, a cyst may eventually form. Joint stress could cause mesenchymal cells to stimulate mucin secretion. Mucin is a constituent of mucus, and mesenchymal cells are cells that can develop into a number of different cell types.
Symptoms of Wrist Ganglion

The lumps associated with ganglion cysts can be characterized by
- Location. Ganglion cysts most commonly develop along the tendons or joints of your wrists or hands. The next most common locations are the ankles and feet. These cysts can occur near other joints as well.
- Shape and size. Ganglion cysts are round or oval and usually measure less than an inch (2.5 centimeters) in diameter. Some are so small that they can’t be felt. The size of a cyst can fluctuate, often getting larger when you use that joint for repetitive motions.
- Pain. Ganglion cysts usually are painless. But if a cyst presses on a nerve — even if the cyst is too small to form a noticeable lump — it can cause pain, tingling, numbness or muscle weakness.
Symptom associate with
- Noticeable swelling or lump.
- The lump is able to change its size, including going away completely only to return.
- The lump is usually soft and immobile.
- In some cases, the lump is painful and aching, particularly those at the base of fingers.
- The ache and pain is made worse by moving any nearby joints.
- The affected tendon may cause a sensation of muscular weakness.
- The back of the hands and wrists are most commonly affected.
- Other sites include the back of the knee (Bakers cyst), ankle, foot, palm and fingers.
Sites of Ganglion Cyst
These cysts most frequently occur around the dorsum of the wrist and on the fingers. A common site of occurrence is along the extensor carpi radialis brevis, as it passes over the dorsum of the wrist joint. Although most commonly found in the wrist, ganglion cysts also may occur in the foot.
Ganglion cysts are “commonly observed in association with the joints and tendons of the appendicular skeleton, with 88% ‘in communication with the multiple small joints of the hand and wrist’ and 11% with those of the foot and ankle.”They commonly are found near the wrist joint, especially at the scapho-lunate area.
In a 2007 study of patients in Glasgow whose foot lumps were being removed surgically, 39 of 101 cases were ganglion cysts. The study replicated earlier findings that no ganglion cysts were found on the sole or heel of the foot; the authors wrote that “Although lumps in these areas may be ganglia, the surgeon should probably consider other diagnoses in the first instance.” The researchers also noted a marked preponderance of occurrence among females (85%) and that 11 of the other cases had been misdiagnosed as ganglion cysts before surgery.
Ganglion cysts are not limited to the hands and feet. They may occur near the knee, commonly near the cruciate ligaments, but also they may occur at the origins of the gastrocnemius tendon and, anteriorly, on Hoffa’s infrapatellar fat pad.At the shoulder, they typically occur at the acromioclavicular joint or along the biceps tendon.
From their common origin at a joint or tendon, ganglion cysts may form in a wide range of locations. Rarely, intraosseous ganglion cysts occur, sometimes in combination with a cyst in the overlying soft tissue. Very rare cases of intramuscular ganglion cysts in the gastrocnemius muscle of the calf have been reported.
Diagnosis of Wrist Ganglion
A physical examination is often all that is needed to diagnose a ganglion.
- Medical history
- Physical examination
- X-rays
- Your doctor may get further confirmation by having a sample of fluid in the cyst tested. An ultrasound scan may be arranged to determine whether the bump is fluid-filled (cystic) or if it is solid. Ultrasound can also detect whether there is an artery or blood vessel causing the lump.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) – is used to see the wrist and is very useful for ganglions.
- If the ganglion cyst is not causing significant pain or discomfort, may not provide treatment, classifying removal of the cyst as a cosmetic procedure.
Treatment of Wrist Ganglion
- Close monitoring – if the ganglion cyst isn’t causing pain or interfering with movement, some doctors prefer to wait and see. The cyst may simply disappear on its own.
- Aspiration – A large, 16 gauge needle is used to aspirate the cyst. This is rarely a permanent solution. In one study with 34 patients, 59 percent of cysts reoccurred within three months.
- Aspiration with a Steroid Injection – This is the most commonly used approach. Thought to be more effective than aspiration alone. However, studies have shown cure rates ranging from 57-79 percent.
- Isometric/ Resistant exercise – of associate muscle is effective for cure of ganglion cyst
- Aspiration – Aspiration alone is one of the simplest ways to treat ganglion. However, it has high recurrence rates. Most of the studies showed more than half of ganglion treated with aspiration alone will recur [rx–rx]. Many methods have been tried in order to increase the efficacy. Zubowicz and Ishii reported a recurrence rate of 15% by repeated aspiration up to three times. However, they also noticed the successful rate decreased with those who needed repeated aspiration [Rx]. Multiple puncture of ganglion wall has not shown to improve the result of simple ganglion aspiration [rx].
- Steroid – Becker suggested the use of steroid injection in treating ganglion, with 87% resolution rate, based on the initial theory that chronic inflammatory may take part in the pathogenesis of ganglion. Subsequent studies showed variable successful rate. Varley et al. conducted a randomized controlled trial to aspiration with or without steroid and concluded that additional injection of steroid is of no benefit and subcutaneous fat atrophy and skin depigmentation can be the potential complications [rx].
- Sclerotherapy – Sclerotherapy has been proposed to treat ganglion. Sclerosant was injected into ganglion sac to damage the intimal lining and cause fibrosis to reduce the recurrence rate. Initial study showed high successful rate ranging 78–100%. Mackie et al., however, confirmed ganglion had no intimal lining by histological studies and reported a failure rate as high as 94%. Since there is communication between ganglion and synovial joint, sclerosant might pass from ganglion to the joint and tendon and cause damage to them [rx]. Since the publication of these reports, the use of sclerotherapy had declined. New technique had been developed with the aim of causing ganglion sclerosis without the risk of damage to the joints. Gümüş used electrocautery to cause ganglion sclerosis and showed favorite results. This technique had not been widely adopted [Rx].
- Hyaluronidase – The content of ganglion may be too vigorous to be drawn, and thus aspiration may not be complete. Some advocated the use of hyaluronidase, which depolymerizes the hyaluronic acid present in ganglion content. Otu reported a 95% cure rate after a follow-up period of 6 months [Rx]. Paul and Sochart also showed that the use of hyaluronidase in conjunction with steroid has resulted in significantly higher resolution rate compared to the use of steroid alone, but only 49% of their patients treated by hyaluronidase and steroid had a complete resolution, compared to 20% in those treated with steroid [Rx]. Akkerhuis et al., however, reported a recurrence rate of 77%, for the treatment of ganglion with hyaluronidase [Rx]. Thus, the successful rate had been variable, and hyaluronidase may cause allergic reaction.
- Immobilization – Immobilization following aspiration had shown conflicting results. Richman et al. showed that 3-week immobilization after aspiration and multiple punctures had a significantly higher success rate for dorsal carpal ganglion, but the result for palmar ganglion was inconclusive [Rx]. On the other hand, Korman et al. concluded that immobilization did not significantly improve the successful treatment of ganglions over perforation and aspiration alone and had the potential adverse effects of inconvenience, economic repercussions, and stiffness [Rx].
- Threat Technique – Gang and Makhlouf introduce the thread technique, by which two sutures were passed through the ganglion at right angles to each other, and each was tied in a loop. The contents of ganglion were expelled by a massage at the interval. They reported a recurrence rate of 4.8%. However, 11% of the patients had positive culture swabs [Rx]. Singhal et al. described a similar technique, but the complete resolution rate was only 50% [Rx].
Review of studies on treatment of dorsal wrist ganglion.
| Method | Recurrence rate (%) | Follow-up |
|---|---|---|
| Aspiration | ||
| 1. Nield and Evans | 59 | 1 year |
| 2. Varley | 67 (no improvement with multiple aspirations) | 4 months |
| 3. Zubowicz | 15 (multiple aspirations) | 1 year |
| 4. Dias and Buch | 47 | 2 & 5 years |
| 5. Westbrook | 49 | 6 weeks |
| Average 41 | ||
| Aspiration and steroid | ||
| 1. Derbyshire | 14 | 2 months–5 years |
| 2. Paul and Sochart | 51 | |
| 3. Wright et al | 83 (even with repeat aspirations) | |
| 4. Breidahl and Adler | 60 | |
| Average 52 | ||
| Aspiration with hyaluronidase | ||
| 1. Otu | 5 | 6 months |
| 2. Paul and Sochart | 51 | 2 years |
| 3. Nelson | 43 | 1–8 years |
| 4. Jagert | 77 | 1 year |
| Average 44 | ||
| Aspiration and sclerosant | ||
| 1. McEvedy | 18 | 13 years |
| 2. Mackie | 93 | 3 months |
| Average 55 | ||
| Aspiration with splinting | ||
| 1. Korman et al | 48 | 1 year |
| 2. Richman et al | 60 | 22 months |
| Average 54 | ||
| Aspiration with multiple puncture | ||
| 1. Stephen et al | 78 | |
| 2. Richman et al | 64 | 22 months |
| 3. Korman et al | 49 | 12 months |
| Average 64 | ||
Surgery of Wrist Ganglion
There are two ways surgery can be used to remove a ganglion cyst
- Open surgery – where the surgeon makes a medium-sized cut, usually about 5cm (2 inches) long, over the site of the affected joint or tendon
- Arthroscopic surgery – a type of keyhole surgery where smaller incisions are made and a tiny camera called an arthroscope is used by the surgeon to look inside the joint; using the arthroscope as a guide, they then pass instruments through the incision to remove the cyst
Ganglion cyst removal is usually an outpatient procedure and may be performed under local or general anesthesia.
Before surgery, your doctor may draw a line above the cyst to mark the incision location. During the surgery, your doctor numbs the treatment area and cuts along the line with a scalpel. The doctor then identifies the cyst and cuts it out along with its capsule or stalk. Once the cyst is removed, your doctor stitches the opening to let the skin heal.
Risk Factors of Wrist Ganglion
As with any surgery, ganglion cyst removal can cause infection. You may experience an allergic reaction to the anesthesia used in the removal, or to the stitches used to seal the removal site. Other possible risks include:
- Sensitivity around scar tissue
- Injuries to surrounding tendons, nerves, or ligaments
- Losing the ability to move the wrist normally
With aspiration
- infection (rare)
- neurovascular injury
With excision
- Infection
- Neurovascular injury (radial artery most common)
- Injury to scapholunate interosseous ligament
- Stiffness
Most likely, you’ll heal quickly and without difficulty after a ganglion cyst removal. The rate of recurrence can vary from person to person. But one study found a 29.7 percent recurrence rate in a sample of 52 participants. Of this group, 60 percent experienced a cyst recurrence within a year of surgical removal.
Home Remedies Wrist Ganglion

Warm Compresses
If you feel the pain caused by a ganglion cyst, you should try warm compresses to find the significant relief. Furthermore, warm compresses are effective in increasing the blood circulation and promoting fluid drainage. As a result, it relieves swelling and pain. Warm compresses also inhibit the growth of a ganglion cyst. Do you want to use warm compresses as one of the amazing natural treatments on how to treat a ganglion cyst?
Here is the instruction
- Let a washcloth soak in the warm water
- Wring out to remove the extra water from the washcloth
- Hold this washcloth over the affected areas for about 10 minutes
- Repeat this treatment 3 or 4 times daily to make the ganglion cysts disappear soon
Frankincense Oil
Frankincense oil is one of amazing home remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst I would like to introduce to you in this article. Frankincense oil not only reduces the pain but also shrinks the size of a ganglion cyst and prevents it from reoccurring. If you want to use frankincense oil as a natural treatment on how to treat a ganglion cyst, you should follow this instruction carefully.
- Apply 2 drops of frankincense oil to a ganglion cyst
- Cover the affected areas with a clean, soft bandage
- Repeat this treatment daily for a few weeks to prevent it from reoccurring
Black Tea Bags
Do you know that black tea bags are considered as one of amazing home remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst naturally? Yes, it is true. Black tea bags contain the acidic properties and the anti-inflammatory effects. Applying black tea bags to the affected areas can relieve swelling and pain.
You should do this:
- Soak black tea bags in the warm water for about 5 minutes
- Remove the excess water from the black tea bags
- Put the black tea bags over the affected areas and hold them for about 10 minutes
- Do this treatment daily for a couple of days
Ginger
Talking about amazing home remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst, you should not ignore ginger. Ginger is well-known for its ability to reduce the discomfort and unbearable pain because it contains the anti-inflammatory properties. To cure a ganglion cyst and prevent it from reoccurring, you can drink ginger tea or take ginger supplements.
Here is the instruction on how to make ginger tea at home.
- First, cut a ginger root into small thin slices
- Put these ginger slices in a cup of water
- Let it simmer for about 10 minutes
- Rinse it off with lukewarm water
You should drink at least 2 or 3 cups of ginger tea daily to get a satisfactory result. It is alright if you want to take ginger supplements. However, it is important for you to consult your doctor carefully before taking.
Turmeric
In this article about amazing natural treatments on how to treat a ganglion cyst, I also want to mention turmeric. Turmeric can help reduce the pain and inflammation caused by a ganglion cyst. It is because of curcumin present in turmeric. Turmeric also has amazing beauty and health benefits. Particularly, turmeric can treat and prevent arthritis symptoms, Alzheimer’s disease, and uveitis. Furthermore, turmeric also reduces the high cholesterol and boosts your immune system.
- Spread a sufficient amount of turmeric over the affected areas
- Leave it for a few minutes
- Rinse it off with lukewarm water
- Repeat this treatment a few times daily for a couple of days
Alternatively, you can drink turmeric tea to fasten the relief. Here is the instruction on how to make turmeric tea:
- Put 2 teaspoons of turmeric into 3 or 4 cups of water
- Boil it and then let it simmer for a couple of minutes
- Strain the tea
- Add squeezed lemon, honey, milk and orange juice to taste it well
- Drink it daily
You can take turmeric supplements. But it is important for you to consult your doctor before applying anything to your skin.
Aloe Vera
Talking about natural treatments on how to get rid of a ganglion cyst, you should not ignore aloe vera. Aloe vera contains anti-inflammatory properties; therefore, it is effective in reducing swelling and pain. Using aloe vera regularly can fasten the healing process for a ganglion cyst.
Here is the instruction:
- Cut an aloe vera leaf and then extract aloe vera gel
- Spread it over your affected areas
- Let it sit on the affected areas for about 20 minutes
- Wash it off with lukewarm water
- Repeat this treatment daily for a couple of days
Epsom Salt
Epsom salt contains the wound-healing properties; therefore, using Epsom salt can help heal a ganglion cyst within a few days. Furthermore, Epsom salt is effective in reducing inflammation and relieving associated pain.
Here is the instruction:
- Add 1 or 2 tablespoons of Epsom salt into 2 cups of water
- Soak a cloth in this solution and then apply it to the affected skin areas
- Hold it for about 20 to 30 minutes
- Do this treatment once daily for a few days
Here is another way:
- Mix 1/3 cup of warm glycerin, ½ teaspoon of Epsom salt and 1/8 teaspoon of borax in a bowl
- Mix all these ingredients together
- Soak a cotton swab in this solution and then apply it to a ganglion cyst on your skin
- Hold a bandage over the affected areas
- Repeat this treatment daily for a couple of days
Castor Oil
Castor oil can be found in health food stores and pharmacies. It can be used as an effective remedy on how to treat a ganglion cyst. You just need to spread a few drops of castor oil over the affected areas and then massage it for a few minutes. Using castor oil on a regular basis can help eliminate ganglion cysts effectively.
Apple Cider Vinegar
Apple cider vinegar is a powerful remedy that can treat millions of diseases. Apple cider vinegar contains anti-inflammatory properties; therefore, it can treat a ganglion cyst.
Here is the instruction:
- Mix apple cider vinegar with baking soda to create a paste
- Add some water into this paste
- Dip a clean cloth into the mixture
- Apply it to the affected skin areas for a few minutes
- Remove it
Do this treatment daily. If you want to have the best result, you should repeat it for at least one month. There are more other home remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst, you should continue reading to know more.
Bromelain
Bromelain is an enzyme present in pineapple. To treat a ganglion cyst natural and effectively, you should consume bromelain daily. Consuming bromelain is one of amazing natural treatment on how to treat a ganglion cyst I would like to introduce to you in this article.
Pencil Eraser
If you see the early signs of a ganglion cyst, you can use the pencil eraser as a simple method on how to treat a ganglion cyst naturally and effectively. Make sure that the rubber is soft. Place this rubber over the affected areas and cover it with a medical gauge. Hold it for a full day. Repeat this treatment for at last one week to get a satisfactory result.
Red Desert Clay
If you are looking for the effective home remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst, you should not ignore red desert clay. Red desert clay is effective in removing the harmful chemicals and toxins from your body. Furthermore, it is loaded with essential minerals that help build your bone and shrink the ganglion cyst size.
Here is the instruction:
- Apply one teaspoon of red desert clay to the affected skin areas
- Keep it for a few minutes
- Rinse it off with lukewarm water
- Repeat this treatment twice daily to get the best result
To fasten the healing process, you can take 5 or 6 red desert clay tablets daily after consulting your doctor carefully.
However, it is important for you to note that red desert clay may cause constipation in some people. To prevent constipation, you should take 1 to 3 teaspoons of magnesium powder daily.
Grapefruit Seed Extract
There are a lot of health & beauty benefits of grapefruit seed extract. Grapefruit seed extract is considered as one of amazing home remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst. Grapefruit seed extract contains antimicrobial properties.
Here is the instruction:
- Apply one drop of grapefruit seed extract to your ganglion cyst
- Use a gauze or band to cover it until the grapefruit seed extract absorbs into your skin completely
You should repeat this treatment daily to get a satisfactory result.
Tea Tree Oil
Tea tree oil is also considered as an effective remedy on how to treat a ganglion cyst I would like to introduce to you in this article. Tea tree oil contains anti-microbial and anti-inflammatory properties. Treat tree oil can treat not only pilonidal cysts but also sebaceous cysts. Here is the instruction on how to use tea tree oil for treating a ganglion cyst.
- Mix 2 drops of tea tree oil with some coconut oil
- Apply this mixture to your ganglion cyst
- Use a band to cover it
- Repeat this treatment daily until a ganglion cyst is treated completely
Lemongrass Essential Oil
If you are looking for the essential oils on how to treat a ganglion cyst, you should not ignore lemongrass essential oil. Lemongrass essential oil is a well-known remedy for muscle pain, slack tissue, and poor circulation. Thanks to pain-relieving effects, lemongrass essential oil is effective in relieving pain caused by a ganglion cyst. Do you want to know how to use lemongrass essential oil for treating a ganglion cyst? Follow this instruction:
- Apply a sufficient amount of lemongrass essential oil to a ganglion cyst
- Keep it for a few hours
- Repeat this treatment daily to get a satisfactory result
There are other essential oils on how to treat a ganglion cyst. You should continue reading to know more.
Thyme Essential Oil
Thyme essential oil is extracted from the leaves of the herb thyme. Thyme oil contains a soothing sensation; therefore, regular application to the affected skin areas can help reduce the pain caused by a ganglion cyst.
Here is the instruction:
- Apply a sufficient amount of thyme essential oil to a ganglion cyst
- Keep it for a few hours
- Repeat this procedure daily to get the best results
Cypress Essential Oil
Cypress essential oil is also one of amazing home remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst. Cypress oil is often used for treating poor circulation. It contains anti-inflammatory, analgesic and diuretic properties. The cypress essential oil is effective in alleviating pain and removing fluid in a ganglion cyst.
Here is the instruction:
- Apply some cypress essential oil to the affected skin area
- Let it sit for a couple of hours
- Do this treatment daily for a few weeks until a ganglion cyst disappears completely
Oregano Oil
If you are looking for the best essential oils on how to treat a ganglion cyst, you should not ignore oregano oil. Oregano oil has anti-tumor properties.
Here is the instruction:
- Mix oregano oil with frankincense oil
- Make this oil mixture hot by putting it in the microwave
- Apply it to your skin
- Keep it for a few hours
If you want to get a satisfactory result, you should repeat this procedure daily. Make sure that you dilute oregano oil before using it topically. This is because applying oregano oil directly to your skin may result in burning sensation.
Natural Herbs Ganglion Cyst
Echinacea
Echinacea helps shrink a ganglion cyst by increasing the level of the properdine chemical in your body and boosting your immune system . Furthermore, the use of Echinacea can stimulate the production of properdine.
Echinacea is one of amazing home remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst I would like to introduce to you in this article. If you are interested in Echinacea, you should follow this instruction:
- Apply over the counter Echinacea ointment topically to the cyst
- Repeat this treatment 3 or 4 times a day if you want to treat a ganglion cyst successfully
Alternatively, you can drink Echinacea tea once or twice a day for at least a week to get a significant improvement.
However, it is important for me to note that people with an autoimmune disorder cannot take Echinacea internally.
Arnica
Arnica contains anti-inflammatory properties; therefore, it is not surprising when arnica is considered as a powerful herb for health and beauty. People often use this herb for treating swelling, pain, and inflammation. Arnica is one of the natural herbs on how to treat a ganglion cyst because it can increase blood circulation.
Here is the instruction:
- Mix arnica essential oil with a sufficient amount of coconut oil or olive oil
- Apply it to the affected areas
- Massage it gently for a few minutes
- Keep a bandage on the affected area
- Repeat this treatment 2 or 3 times daily for a few days
Alternatively, you can test arnica on your wrist before trying it on your larger areas. Arnica may cause irritation and itchiness in some people.
Hazel Of White Oka Bark Tea
It is an old way on how to treat a ganglion cyst at home. Hazel of white oka bark tea is effective in reducing the size of a ganglion cyst. When the size of a ganglion cyst becomes smaller, it can easily be removed. Do you want to know how to use hazel of white oka bark tea for treating a ganglion cyst? It is simple and easy. You just need to apply a sufficient amount of hazel of white oka bark tea to your ganglion cyst. Let it sit for a couple of minutes. To get a satisfactory result, you should repeat this treatment daily for a few weeks.
Witch Hazel
Witch hazel is one of the amazing herbal remedies on how to treat a ganglion cyst I would like to introduce to you in this article. There are many benefits of witch hazel for skin care. The tannins present in witch hazel contain astringent properties; therefore, applying witch hazel can help tighten your skin and limit the secretion of oil that results in a ganglion cyst. Furthermore, not only the leaves but also the bark of witch hazel contains therapeutic properties that can treat a ganglion cyst.
References
[bg_collapse view=”button-orange” color=”#4a4949″ expand_text=”Show More” collapse_text=”Show Less” ]
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4045351/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2682407/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK470168/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4916095/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4085360/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5799836/
[/bg_collapse]